A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And the process is known as recursion.
Working of Recursion in Python
def recurse():
...
recurse()
...
recurse()
The recurse() function calls itself over and over again. The figure below shows how recursion works.
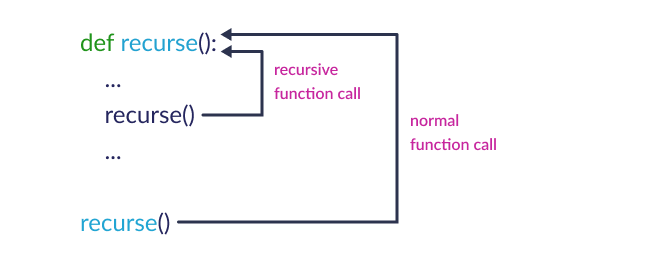
Example: Recursion
def greet():
print('Hello')
# recursive call
greet()
# normal function call
greet()
Output
Hello Hello Hello Hello .. ..
The above program will call itself infinitely. Hence, we must include a stopping condition to stop the recursive call.
Stopping Condition for Recursion
If we do not include a stopping condition to stop the recursive call, the function will keep calling itself infinitely.
We generally use the if...else statement to stop the recursion.
def recurse():
if condition:
# condition to break recursion
else:
# recursive call
recurse()
In the above code, the if statement stops the recursive call and the else statement calls the function recursively.
Example: Recursion With Stop Condition
def print_number(number):
# print number
print(number)
# stopping condition
if number == 0:
print('Stop Printing')
else:
# recursive call
print_number(number - 1)
print_number(2)
Output
2 1 0 Stop Printing
In the above example, we have created a recursive function named print_number(). Here, the function calls itself until the number passed to it becomes 0.
Working of the code:
| Function call | Prints | number == 0 ? |
|---|---|---|
print_number(2) |
2 | False |
print_number(2 - 1) |
1 | False |
print_number(1 - 1) |
0Stop Printing |
True [function call stops] |
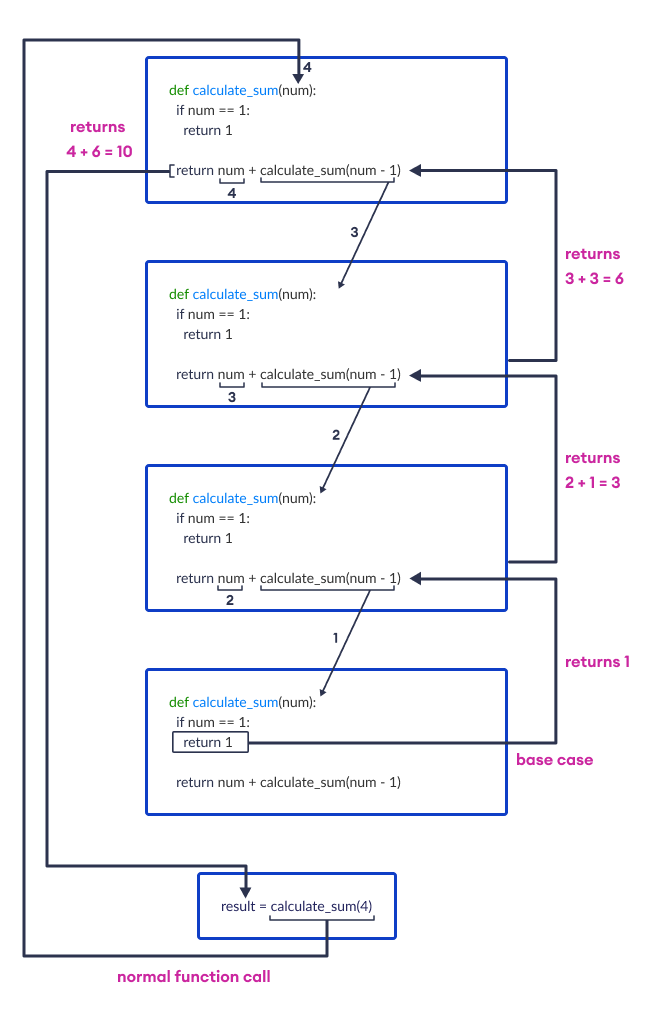
Example: Sum of Natural Numbers
def calculate_sum(num):
# stopping condition
if num == 1:
return 1
# recursive call
return num + calculate_sum(num - 1)
result = calculate_sum(4)
print(result)
Output
10
The calculate_sum(num) function calculates the sum of all integers from num to 1 using recursion.
If num equals 1, it simply returns 1 since that's the base case. Otherwise, it returns num plus the result of a recursive call to calculate_sum(num - 1).
Here, calculate_sum(4) computes the sum of 4, 3, 2, and 1, which is 10.
Working of the Sum of Natural Numbers
Advantages and Disadvantages of Recursion
The advantages and disadvantages of using recursion in Python are as follows:
Advantages
- Recursion makes our code shorter and cleaner.
- It is required in data structures and algorithms, such as Graph and Tree Traversal.
Disadvantages
- Recursion uses more processor time.
- Recursive functions are more difficult to debug compared to an equivalent iterative program.