In R programming, while loops are used to loop until a specific condition is met.
Syntax of while loop
while (test_expression)
{
statement
}
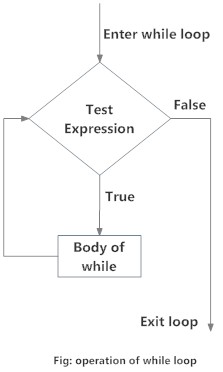
Here, test_expression is evaluated and the body of the loop is
entered if the result is TRUE.
The statements inside the loop are executed and the flow returns to evaluate
the test_expression again.
This is repeated each time until test_expression evaluates to
FALSE, in which case, the loop exits.
Flowchart of while Loop
Example of while Loop
i <- 1
while (i < 6) {
print(i)
i = i+1
}
Output
[1] 1 [1] 2 [1] 3 [1] 4 [1] 5
In the above example, i is initially initialized to 1.
Here, the test_expression is i < 6 which
evaluates to TRUE since 1 is less than 6. So, the body of the
loop is entered and i is printed and incremented.
Incrementing i is important as this will eventually meet the exit
condition. Failing to do so will result into an infinite loop.
In the next iteration, the value of i is 2 and the loop
continues.
This will continue until i takes the value 6. The condition
6 < 6 will give FALSE and the while loop finally
exits.
Check out these examples to learn more: